Resources > What is an HSE?
What Is HSE? Meaning of Health, Safety & Environment (HSE)
HSE stands for Health, Safety and Environment. It’s the umbrella term for the policies, procedures, and culture organisations use to protect people’s health, keep work environments safe, and reduce environmental risk and impact.
HSE isn’t a tick-box exercise—it’s how you prevent incidents, meet regulations, and build trust with employees, contractors and visitors.
What does HSE stand for?
HSE = Health, Safety & Environment.
You’ll also see EHS used interchangeably (same three pillars, different order). In the UK, HSE can also refer to the Health and Safety Executive, the national regulator.
What is HSE? A simple definition
HSE is a management approach that:
-
Protects people from injuries and ill health at work.
-
Protects the environment (pollution prevention, waste control, emissions management).
-
Reduces risk through systematic identification, assessment, control and continuous improvement.
Strong HSE programmes blend policy, training, controls, monitoring, and clear accountability—backed by reliable data and audit trails.
Why HSE matters (work, health, environment & risk)
-
Work: Fewer incidents, less downtime, stronger compliance culture.
-
Health: Reduced exposure to hazards; ergonomics and wellbeing built into daily operations.
-
Environment: Measurable reductions in waste, spills and emissions; alignment with ISO 14001 and ESG goals.
-
Risk: Proactive identification, documented controls and evidence you’re doing the right things consistently.
HSE in the workplace
Practical building blocks include:
-
Risk assessments and method statements
-
Incident & near-miss reporting with investigation and CAPA
-
Audit & inspection programmes
-
Training & competency tracking
-
Permit-to-work and contractor control
-
Environmental monitoring (waste, water, air, spills)
Done well, these steps create a feedback loop that drives down risk and improves performance over time.
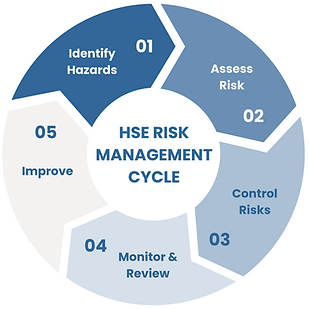
The HSE risk management cycle (quick guide)
1. Identify hazards:
Where and how could things go wrong?
2. Assess risk:
Likelihood × severity using a consistent matrix
3. Control risks:
Hierarchy: eliminate, substitute, engineer, admin, PPE
4. Monitor & review:
Inspections, LTIs/near misses, trend analysis
5. Improve:
CAPAs, MoC, refresher training, leadership reviews
If it isn’t recorded, it didn’t happen—consistency and evidence are key.
How software helps: EHS SmartStart
Manual spreadsheets make HSE slow and error-prone. EHS SmartStart brings everything into one configurable, cloud platform so you can streamline compliance, improve safety and reduce risks—fast.
Core modules (mix & match)
-
Compliance Management – Centralise legal duties, manage permits/inspections, track obligations, stay audit-ready.
-
Audit Management – Custom checklists, real-time findings, CAPA tracking and escalation.
-
Incident Management – Capture incidents and near misses, track LTIs, investigate root causes, drive corrective actions.
-
Risk Management – Plan and maintain risk assessments, link controls, monitor residual risk.
-
Management of Change – Assess and approve operational changes with built-in risk checks.
-
Projects & Actions – Plan EHS initiatives, assign owners, automate reminders, maintain full audit trails.
-
Global Standards & Programs – Roll out corporate standards globally and map them to local programmes.
Environmental features
-
Environmental risk assessments and aspects/impacts registers
-
Environmental MoC and regulation repositories
-
Audit-ready records aligned to ISO 14001 and ESG reporting
-
Environmental incident logging with CAPA
Why teams choose EHS SmartStart
-
Out-of-the-box in a day yet fully configurable (no fragile custom code)
-
Secure Azure hosting, role-based access, multi-site and multi-language
-
Real-time analytics & dashboards for transparent decision-making
-
Scales from a single site to global operations
FAQs: HSE basics
What is HSE?
HSE is the integrated approach to protecting people’s health, ensuring safety at work, and managing environmental responsibilities—by identifying, controlling and continuously reducing risk.
What does HSE stand for?
Health, Safety and Environment. (Also called EHS; same scope.)
Is HSE the same as EHS?
Yes—two acronyms for the same three pillars.
Who is responsible for HSE?
Everyone. Leaders set policy and resources; managers implement; employees and contractors follow procedures and speak up; specialists provide governance and assurance.
How do I start improving HSE today?
Standardise risk assessments, log every incident/near miss, run scheduled audits, track actions to closure—then centralise it all in EHS SmartStart to make it consistent, measurable and auditable.
